Vaccines have transformed global health by providing immunity against a wide range of infectious diseases. While traditional vaccines rely on live attenuated or inactivated pathogens, modern immunology has highlighted the critical role of adjuvant vaccines in enhancing immune responses. Adjuvants are substances added to vaccines to boost the body’s immune reaction, improving both the magnitude and durability of protection.
GC Biotech, a leader in advanced vaccine technologies, has been at the forefront of developing adjuvanted formulations that optimize immunogenicity while ensuring safety and regulatory compliance. Their solutions are widely used in both human and veterinary medicine to meet the growing demand for effective, long-lasting immunization.
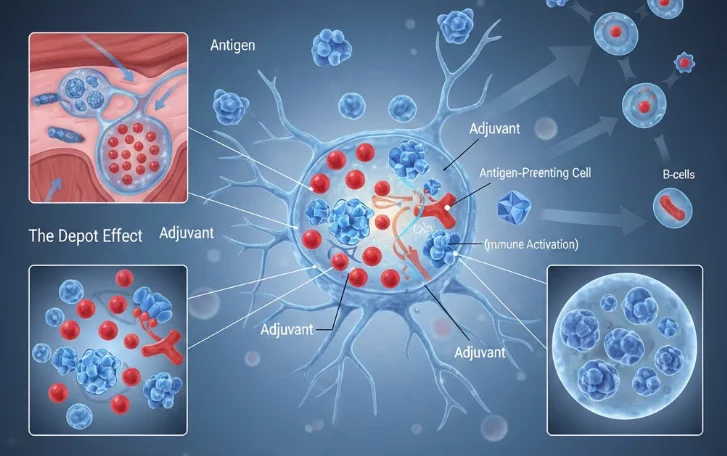
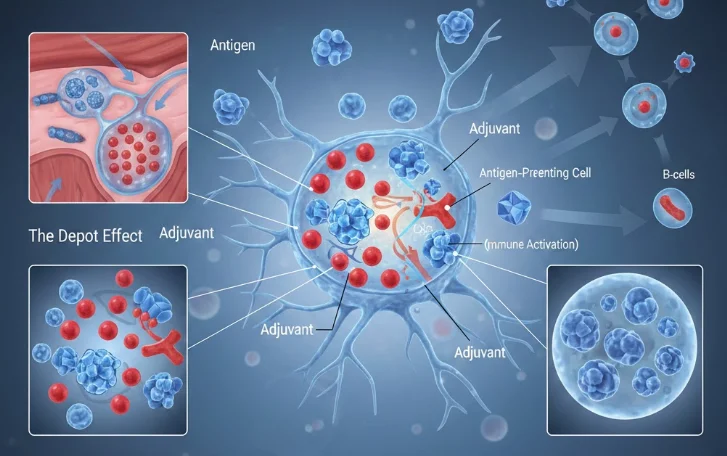
2. Understanding Adjuvant Vaccines
What Are Adjuvants
Adjuvants are compounds incorporated into vaccines to:
-
Enhance the immune system’s recognition of antigens
-
Increase antibody titers and cellular immunity
-
Reduce the amount of antigen required per dose
-
Enable broader protection against variable pathogens
Commonly used adjuvants include aluminum salts (alum), oil-in-water emulsions, saponins, and novel nanoparticles, each with unique mechanisms of action.
Mechanisms of Action
Adjuvants work through multiple pathways:
-
Depot Effect: Prolongs antigen exposure at the injection site, sustaining immune activation.
-
Immune Cell Recruitment: Stimulates dendritic cells and macrophages to process and present antigens effectively.
-
Cytokine Modulation: Enhances the production of signaling molecules that regulate adaptive immunity.
-
Toll-Like Receptor Activation: Triggers innate immune pathways, creating a robust and balanced immune response.
By combining these mechanisms, adjuvant vaccines improve vaccine efficacy, particularly in populations with weaker immune responses, such as the elderly or immunocompromised.
3. Advantages of Adjuvant Vaccines
Enhanced Immunogenicity
Adjuvants increase the strength and duration of the immune response, often allowing for fewer booster doses and reducing vaccine wastage.
Dose-Sparing Effect
By amplifying antigen presentation, adjuvanted vaccines require lower antigen quantities, which is crucial during pandemic scenarios where vaccine supply is limited.
Broad-Spectrum Protection
Certain adjuvants improve the immune system’s ability to recognize multiple strains of a pathogen, offering cross-protection against evolving variants.
Safety and Tolerability
Modern adjuvants are carefully formulated to minimize side effects while maximizing efficacy. Companies like GC Biotech conduct extensive preclinical and clinical trials to ensure formulations meet rigorous safety standards.
4. Applications Across Medicine
Human Vaccines
Adjuvants are widely used in vaccines for influenza, hepatitis B, human papillomavirus (HPV), and emerging infectious diseases. Their ability to boost immunogenicity is especially valuable in populations with compromised immunity.
Veterinary Vaccines
In veterinary medicine, adjuvant vaccines help protect livestock and companion animals against economically significant diseases. Enhanced immune responses reduce disease outbreaks and improve herd immunity.
Experimental and Therapeutic Vaccines
Emerging research explores adjuvants in cancer vaccines, allergy immunotherapies, and autoimmune disease modulation, demonstrating their potential beyond infectious disease prevention.
Formulation Considerations by GC Biotech
Designing adjuvant vaccines involves a balance of efficacy, safety, and stability:
-
Selection of Adjuvant Type: Choice depends on antigen properties, desired immune response (humoral vs. cellular), and administration route.
-
Compatibility Testing: Ensures the adjuvant does not degrade the antigen or provoke excessive inflammation.
-
Stability and Storage: Formulations must remain stable under recommended storage conditions, preserving both antigenicity and adjuvant activity.
-
Regulatory Compliance: Adjuvant vaccines are subject to stringent evaluation by regulatory authorities such as the FDA, EMA, and WHO guidelines.
GC Biotech applies cutting-edge formulation technology to optimize adjuvant-antigen interactions, producing vaccines that are effective, safe, and scalable for global distribution.
Challenges and Innovations
While adjuvants provide significant benefits, their development faces challenges:
-
Reactogenicity: Some adjuvants may cause local or systemic reactions, requiring careful dose optimization.
-
Population-Specific Responses: Immune responses can vary across age groups, species, or genetic backgrounds.
-
Emerging Pathogens: New diseases demand adjuvants that can rapidly induce broad immunity.
Innovations focus on nanoparticle-based adjuvants, liposome carriers, and TLR agonists, which enable targeted immune activation with minimal side effects.
Conclusion: Maximizing Vaccine Impact
Adjuvant vaccines represent a critical advancement in immunology, allowing enhanced protection, reduced dosing, and broad-spectrum immunity. Through expertise in formulation and clinical application, GC Biotech ensures that these vaccines meet the highest standards of efficacy, safety, and reliability. As infectious diseases continue to evolve, adjuvanted vaccines will remain central to global health strategies, safeguarding populations and supporting resilient healthcare systems.
https://en.jicangbio.com/enhancing-immunity-the-role-of-adjuvant-vaccines-in-modern-healthcare.html